What is Niacin?
Is a water-soluble B Vitamin (B3) and an essential human nutrient. The primary role of Niacin is to turn food into energy needed by our cells. Unfortunately, Niacin or Vitamin B3 must be obtained from dietary sources since the human body cannot synthesize it on its own. Yet, there are plenty of niacin benefits for hair, and today, more evidence and research are coming to light regarding niacin topicals for hair growth.
What Foods Are High in Niacin?
 Niacin can be found in green leafy vegetables and other healthful food sources.
Niacin can be found in green leafy vegetables and other healthful food sources.What Foods Are High in Niacin?
Niacin can be naturally found and implemented into your diet from a variety of natural, unprocessed foods such as:
- Liver
- Chicken breast
- Tuna
- Turkey
- Salmon
- Anchovies
- Pork
- Ground Beef
- Peanuts
- Avocado
- Brown Rice
- Whole Wheat
- Mushrooms
- Green Peas
- Potatoes
Niacin, as well as niacinamide, are also available to consumers as supplement products.
How Does Niacin Work Within The Body?
Within the body, vitamin B3 combines with nicotinic acid to form niacinamide, also known as nicotinamide. Unlike what people may believe, niacinamide does not cause hair loss. In fact, research may suggest otherwise. Nicotinamide has many reported health benefits and effects and has received much attention as a skin, hair, and beauty ingredient. This is one of the reasons why experts believe that niacin could perhaps help with hair health, hair growth, hair restoration, and more. Today, there are many studies that may state how niacin is good for the hair, as well as support how niacin benefits hair follicle health.
Research on Topical Niacinamide for Hair Growth in Women
 Niacin may potentially help women suffering from alopecia hair loss.
Niacin may potentially help women suffering from alopecia hair loss.In a research study called, A pilot study evaluating the efficacy of topically applied niacin derivatives for treatment of female pattern alopecia, 60 women at various stages of pattern hair loss (Ludwig types 1-3) participated in a double-blind, placebo-controlled study on the effects of nicotinate [1] on hair health and hair loss.
In women, pattern hair loss (androgenic alopecia) manifests as thinning hair density, increased shedding, and hair strands with reduced volume. So far, Minoxidil 2% is the only approved treatment for this condition. As discussed earlier, nicotinic acid combines with Niacin to form nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide. The anionic form of this acid is nicotinate which was observed in this study.
The researchers observed the topical effects of octyl nicotinate. First, they divided the female participants into two groups:
- Treatment group who received a topical solution of the octyl nicotinate
- Control group who received an inactive vehicle solution
After 6 months, the Niacin derivative solution induced a significant increase in hair fullness within the treatment group subjects. The researchers are not clear on the exact mechanism of action, but they speculate that the treatment formula may have helped improve the density of the follicles and the quality of existing hairs. This shows that nicotinic acid derivatives could be a potentially viable treatment for female alopecia, confirming how niacin benefits for hair can be effective. Yet, continued studies on larger sample sizes are still needed at this point to directly confirm niacin's influence on hair health and hair growth.
A Study on a Niacin Topical Hair Growth Formulation
In another study, A Novel Cosmetic Approach to Treat Thinning Hair, a group of researchers designed a topical leave-in formulation to treat hair strands with diminished diameters [2]. This consisted of the following set of ingredients (CNPDA):
- Caffeine
- Niacinamide
- Pantheon
- Dimethicone
- Acrylate polymer
The research team hoped to find a new way to address thinning hair in women. Existing hair loss treatments usually attempt to improve hair density or prevent further damage. So far, there are no solutions that actually address the thinning diameter of the hair shafts. This group of scientists was optimistic that they could devise a Niacin-based formula to help address this diminishing hair strand thickness.
They measured hair fiber diameters using a laser scan micrometer. They also used the tensile break stress and torsion pendulum testing methods to determine improvements in mechanical and behavioral properties. Based on their data, the researchers found that the CNPDA treatment could increase hair strand diameters by 2-5 um, expanding their cross-sectional areas by about 10%. The treated hairs also displayed the characteristic properties of thicker hair with improved subtleness, pliability, and ability to withstand force without breaking.
Niacin HDL and Why It Matters For Hair Loss
 Low HDL levels (good cholesterol) may be linked to hair loss. Niacin may help provide treatment benefits.
Low HDL levels (good cholesterol) may be linked to hair loss. Niacin may help provide treatment benefits.Niacin benefits for hair may help reduce hair loss by improving high-density lipoproteins, also known as HDL cholesterol, or “good cholesterol” in the body. A study called, Both low circulating insulin-like growth factor and high-density lipoproteins are associated with hair loss in women. In addition, a group of scientists discovered a strong correlation between low HDL levels and hair loss in females [3]. They closely examined 323 middle-aged women and found that the subjects with lower than average HDL cholesterol were more likely to suffer from hair loss compared to the female participants with normal levels of good cholesterol. Since niacin is commonly used to boost HDL cholesterol, this nutrient may prevent or even reverse hair loss in women. However, further research would be needed to see if this could be a cause-and-effect relationship.
Niacin and Its Role In Keratin Production
In its amide form, Niacin helps to facilitate and speed up the synthesis of keratin(keratinization) in the hair follicles, which is needed to form the visible hair strands. This process centers around a cell division mechanism at the base of the follicles. The derma papilla cells emit a hormonal signal to the stem cells, which causes them to differentiate into progenitor cells. These progenitor cells divide and split into two daughter cells. One will retain the nucleus, and the other will die, forming a container of keratin (keratinocyte). This buildup of keratin forms new hair strands.
Niacin’s job is to help keep this process moving. A lack of niacin in the body reduces the proper movement in this bodily process and will result in weak, thin strands of hair that are much more susceptible to hair falling and hair loss.
Cons of Taking Niacin
Although Niacin offers many positive benefits (e.g., it lowers bad cholesterol, turns food into energy), it may also cause various unwanted side effects such as:
- Irregular heartbeats
- Vision problems
- Jaundice (yellowing eyes or skin)
- Lightheadedness
- Skin redness or flushing
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Dry itching skin
- Headaches
- Skin discoloration
Do not take Niacin if you are pregnant or breastfeeding. Also, avoid consuming alcohol if you decide on supplements. An additional set of risk factors include:
- Niacin allergies
- Advanced liver disease
- Active bleeding
- Stomach ulcers
Niacin is also contraindicated for minors under the age of 18.
Safety Profile for Niacin
In their Skin Deep ingredient assessment, the Environmental Working Group (EWG) gives Niacin a toxicity/hazard score of 1 out of a scale of 10. Overall, this ingredient is regarded as being generally safe in terms of its potential risk for areas such as:
- Cancer
- Developmental/reproductive toxicity
- Immunotoxicity
- Allergies
- Environmental toxicity
- Bioaccumulation and persistence
Also, according to the FDA, Niacin is safe for "general or specific, limited use in food." However, as with any supplement, Niacin is associated with side effects, as noted above. Discuss with your doctor safe dosage limits, time constraints, and any other pre-existing health concerns that may interfere with your usage of this supplement.
Other Uses of Niacin
Niacin is used as a natural (secondary) treatment intervention for health issues such as:
- Premenstrual syndrome
- Memory problems
- Cataracts
- Diabetes
- Alzheimer's disease
- Arthritis
- Acne
- Migraines
- Motion sickness
Due to its potential for undesirable side effects, speak to your doctor before taking Niacin supplements. Also, be sure to consider the effects of processing on the final quality, whether it is Niacin or another natural ingredient.
How Niacin Improves Blood Flow
 Researchers are finding that niacin may help improve blood flow to the scalp for healthier hair.
Researchers are finding that niacin may help improve blood flow to the scalp for healthier hair.Niacin helps blood vessels dilate, which helps to improve blood circulation throughout the body. Additionally, its derivative, nicotinic acid, can also reduce blood thickness (i.e., viscosity), facilitating blood flow. Healthy hair depends on blood circulation to deliver oxygen and nutrients needed by the follicle to function properly. By helping to stimulate blood circulation, Niacin contributes to optimizing hair growth processes.
Niacin Benefits for Hair: Repairs DNA Damage
Niacin also helps repair DNA damage which can decrease the protein levels necessary for the healthy production of hair. Our DNA contains code sequences for building all the proteins in the body. Damage to the DNA, which occurs through natural aging processes, UV radiation, and free radicals, can hinder the construction of important protein structures, whether they are used for hair or other parts of the body. In summary, DNA damage can decrease the protein levels necessary for the healthy production of hair. Niacin is used to make a coenzyme called NAD (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide), which plays a primary role in oxidative phosphorylation, converting food-derived components like fatty acids and glucose into energy. More so, research shows that the body engages in heightened levels of oxidative phosphorylation in response to damaged DNA. Niacin, therefore, helps to restore normal protein production by serving as a crucial building block for DNA repair processes.
VIDEO: Watch This Woman Get Her Edge Back Using Natural Pomade - Dr.UGro Gashee Product With Niacin
Meet Diane, one of our Gashee True Life Stories. As a traction alopecia sufferer, she was distraught at the sight of her lost edges. After using Minoxidil for a year, she saw no improvement. However, she decided to give our Dr.UGro Gashee pomade a try, making a real difference in her appearance. Niacinamide, combined with natural botanical extracts, contributed to these improvements.
Diane noted that before, her hair was "never thick...[she] never had thick consistency of hair." Within a few months of using the product, she states that she "noticed drastic improvements - initially [she] saw that her hair was fuller - and there was a clear difference in the hair between the picture that was initially taken." More so, she states that the GASHEE Pomade that she used was very easy to apply: "take a small amount, rub it in my fingertips, and apply to hair as needed!" Now Diane feels that the natural pomade has changed her for the better, in how she sees herself, and she is now "confident in appearing to the outside world."
GASHEE Natural Pomade Before and After Hair Growth Results
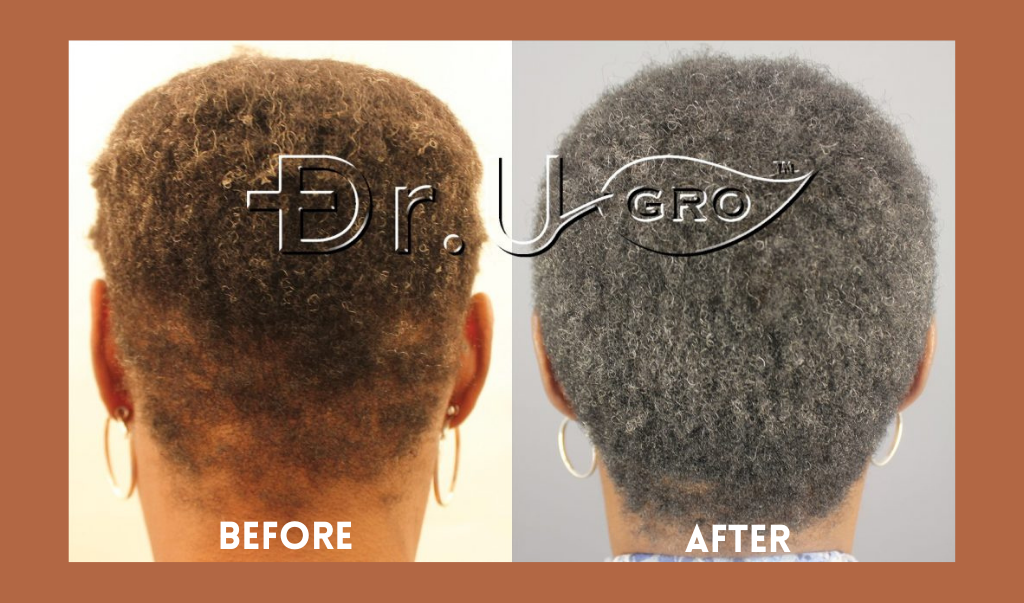 Diane Before and After several months of using Gashee All Natural Pomade*
Diane Before and After several months of using Gashee All Natural Pomade*Note the thicker consistency of her hair, as well as the regrowth and filling of previous patches of lost hair on her scalp.
What makes GASHEE Different?
GASHEE Have Been Studied & Tested for Hair Growth!
Dr.UGro’s All-Natural Gashee hair health topicals have been clinically tested and researched in regards to its hair growing effectiveness. The study, published in 2021 in the Hindawi Case Reports in Dermatological Medicine concluded that “significant improvements in hair regrowth in the nape, crown, vertex, and temple areas” were observed in nearly all patients after 3-15 months of treatment using these products [5].
If you are looking to utilize niacin benefits for hair, to regrow or restore your hair, or want to help maintain your hair's natural beauty, try Dr. UGro GASHEE lotion or pomade today.
Frequently Asked Questions - Niacin Benefits for Hair Follicle Health
How many mg of niacin for hair growth should I take daily?
Although Niacin is considered a vitamin and a nutrient that we need for our health, over-dosage can lead to adverse health effects. These adverse side effects include flushing, upset stomach, liver dysfunction, glucose intolerance, and blurred vision. The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for an adult male is 16mg/day. The RDA for adult females is 14mg per day, while the Tolerable Upper (TU) upper intake level of niacin has been determined to be 35 mg/day.
The consumption of niacin through food sources is likely to be safe, but using supplements with niacin should be discussed with your physician, who can recommend an appropriate dosage for your particular health needs. For these reasons, you may find topical hair products to be the best method to deliver niacin to the hair. There is less chance of systemic side effects from niacin if applied through a topical product. Some natural hair products have made optimal use of niacin in their formulation to excellent effect on hair health.
Does nicotinamide cause hair loss?
There are no studies that support nicotinamide as a cause of hair loss. In fact, research, such as the studies discussed above, actually suggests that nicotinamide supports hair growth as a topical treatment and within the body’s own natural processes.
Are Niacin benefits for hair limited to the hair strands? Can the nutrient also help the hair follicle?
Researchers have found that nicotinamide can exert photoprotective properties [4]. And as an ingredient in sunscreens, it can also offer improved protection for the epidermal barrier of the skin’s surface, which also benefits the hair follicles, keeping them safe from the damaging effects of UV rays.
Related Articles on Hair Loss & Restoration
For additional information regarding hair loss and restoration ingredients that you may find useful, check out the articles below.
References
- Draelos et al., A pilot study evaluating the efficacy of topically applied niacin derivatives for treatment of female pattern alopecia, Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 4(4): 258-61, Jan. 2006
- Davi MG, et al., A novel cosmetic approach to treat thinning hair, BrJ. Dermatol 2011 Dec; 165 Suppl 3:24-30
- Noordman et al., low circulating insulin-like growth factor, and high-density lipoproteins are associated with hair loss in women, Br. J Dermatol. 2016
- Gehring W., Nicotinic acid/ niacinamide and the skin, J.Cosmet. Dermatol: 2004 Apr. 3(2) 88-93
- Umar, S. and Carter, M., 2021. A Multimodal Hair-Loss Treatment Strategy Using a New Topical Phytoactive Formulation: A Report of Five Cases.





