The Role of Methionine in Your Journey Towards Better Hair
Your hair and hair follicles are made up of proteins formed by building blocks called amino acids. Therefore, when you optimize your intake of amino acids, your body can have enough resources to create proteins. Methionine is an example of an amino acid that plays an extremely important role in your physiology and the well-being of your hair.
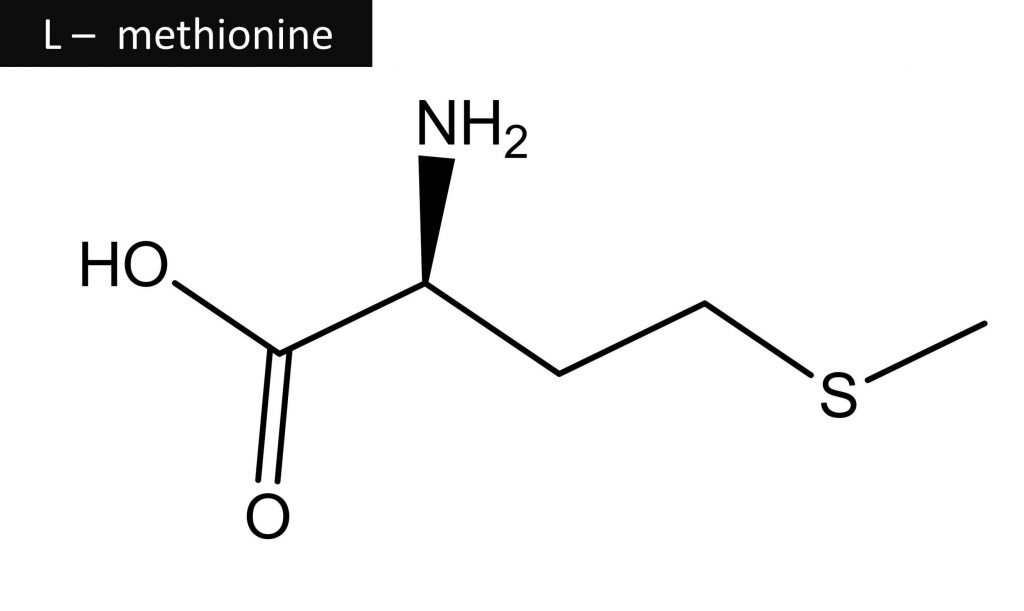
Methionine, an essential amino acid, is being studied by scientists for its potential effects on hair growth.
What Is Methionine?
Methionine is considered an essential amino acid, meaning it cannot be produced by the body and must be consumed through dietary means. Common foods rich in this amino acid include meat, fish, and dairy products. Examples of plant-based foods that provide excellent sources of methionine include Brazil nuts, sunflower seeds, quinoa, and buckwheat.

Sunflower seeds and other food sources provide excellent sources of methionine
Methionine is necessary for many important functions in our body. This includes our metabolism, cell reproduction, tissues, and the proper absorption of zinc and selenium. It is also involved in the initial steps of building new proteins in our cells to replace older structures that break down over time.
The DNA code for methionine is AUG, the signal to start the protein-building process. The instructions in our genes to create most protein structures begin with this code. It is the first to be transcribed (i.e., read) by the mRNA in the protein-building process.
Methionine also acts as a substrate to produce other amino acids and various sulfur-containing compounds that our cells rely on to function properly. These special compounds also protect our tissues, modify our DNA, and maintain the normal processes of our cells. They include:
- cysteine
- taurine
- glutathione
- SAMe
Due to the importance of these compounds for our health, many experts recommend taking methionine supplements to help the body produce even more of them.
Methionine Creates Four Important Molecules That Our Bodies Need
Methionine is needed to create four compounds which our hair follicles and the rest of our cells and tissues depend on for normal, healthy functioning.
Cysteine
Produced from methionine, cysteine is an important sulfur-containing amino acid used to create taurine, glutathione, and other protein structures. Two cysteine molecules form a new type of amino acid, known as cystine, which is used for the structures of our hair, skin, and nails. The disulfide bonds of the cysteine molecule hold the hair strand together. They consist of two sulfur atoms, each attached to a cystine component molecule. Chemical treatments like hair relaxers, straighteners, and perms alter the disulfide bonds to create new hair textures.
Taurine
Taurine is another amino acid created from methionine. It plays an important role in our metabolic processes, nervous system as well as our heart and circulatory system. The hair follicle takes in taurine from the bloodstream and incorporates it into the connective tissue sheath, the hair bulb, and the outer root sheath. It supports hair survival and protects the follicle from the effects of TGF-B which slows hair growth.
Glutathione
Glutathione is referred to as the “master antioxidant”, defending our bodies from oxidative damage caused by free radicals. It is also involved in the production of protein and DNA as well as the metabolism of nutrients. All of these are important functions that our hair follicles need to thrive. In one study, researchers looked at different types of glutathione across 27 men and women, 19-102 years in age. Based on their findings, they concluded that the keratinocytes of the hair follicle are endowed with an intrinsic ability to detoxify, as a result of glutathione [1]. However, this ability is age-related. In a similar study, researchers found that glutathione has an important role, protecting hair follicle cells during aging processes. They also confirmed that it decreases with age. However, hair follicles retain the ability to protect themselves from peroxides over time.
SAMe(S-Adenosylmethionine)
SAMe is found throughout the fluids, cells, and tissues of the body, participating in many types of biochemical reactions by transferring a part of itself to other molecules, such as DNA and proteins. It is needed for creatine production and cellular energy. Additionally, SAM helps our immune system function properly. Overall, it helps our cells defend themselves against destruction and damage. SAMe is involved in a process called methylation, donating a methyl group to other compounds. Methylation is necessary for synthesizing DNA, RNA, phospholipids, proteins, hormones, neurotransmitters, and glutathione. It also promotes gene expression, lipid, and mineral metabolism. SAMe is also needed to create polyamine compounds which regulate the life cycles of our cells, including apoptosis, or programmed cell death. Polyamines also repair DNA, promote gene expression, and phosphorylate proteins. One type of polyamine, called spermidine, has even been referred to as a “universal anti-aging drug” since it has shown to promote longevity across many living systems, including single cells.

Methionine may influence gene expression and enhance our ability to grow hair.
Lastly, the methylation capacities offered by SAMe helps our DNA adapt and evolve. Adding a methyl group to DNA is an epigenetic mechanism that enables necessary changes to be made in the sequencing of our gene codes [2]. This capability gives our physiology greater flexibility in how it responds and adapts to environmental changes. In one study, researchers came up with a hypothesis that DNA methylation varies in different regions of the scalp [3]. This would explain why men with androgenetic alopecia experience hair loss in the vertex, but not the occipital regions. Their results suggest that increased levels of AR methylation protect occipital hair follicles from miniaturization. Such findings imply that it may be possible to apply the principles of DNA plasticity through methylation to topical formulations in the therapeutic treatment of androgenetic alopecia.
Benefits of Methionine and the Structure of Our Hair

Methionine contributes to healthier and stronger hair, and to the overall well-being of our body.
Keratin is the protein that makes up most of the structure of our hair. One study reveals a rather profound relationship between methionine and the structural integrity of the protein compound of keratin. Researchers found that demethylation of methionine leads to damaged keratin in human hair.
The central importance of methionine lies in its ability to initiate protein production and create several important molecules we need to maintain and even enhance the healthy functioning of our cells. We should strive to improve our methionine intake for the sake of our hair and for the health of our entire body. While methionine can be obtained from dietary sources, optimal levels can also be achieved through natural and comprehensive dietary supplement products.
Loss of Methionine and Graying Hair
Researchers have found that the reduction of methionine in the body leads to an accumulation of hydrogen peroxide in hair follicles [3]. Furthermore, an enzyme known as tyrosinase becomes less effective. These changes contribute to the loss of pigmentation in hair, causing it to turn gray and white. Methionine levels in your body can be enhanced through dietary intake. When considering a supplement product, be sure to hone in on the quality of its formulation, the bioavailability of its ingredients, and its overall attunement with the natural needs of your body.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is more methionine better when it comes to dietary intake?
As with any form of nutritional intake, the key to remember is balance. Excessively high methionine consumption may lead to toxic effects. Studies on animals actually show that lowering methionine can lead to improved health benefits. Examples include slower aging processes and an expanded lifespan. However, further studies are needed to generalize these findings to humans.
How much methionine should I be taking?
The daily recommended intake of methionine plus cysteine is 8.6 mg/lb (19 mg/kg) per day for adults, which is about 1.3 grams for an individual weighing about 150 pounds. Elderly men and women may require higher intakes of methionine at 2 to 3 grams per day.
I am a vegan. What are some good sources of dietary methionine?
There are certainly plant-based sources of this amino acid. Some examples include wheat gluten, spinach, Brazil nuts, spinach, oats, and sunflower seeds, to name a few. However, you will need to consume large amounts of these types of foods to obtain the correct levels of methionine. Vegans, vegetarians, and plant-based eaters should regularly consult with their physician to ensure that their individual dietary needs are properly met.
References
[1] F. Pruche, M. Kermici, (June 1991) Changes in glutathione content in human hair follicle keratinocytes as a function of age of donor: relation with glutathione dependent enzymes, Int. J Cosmet. Sci, 1991 Jun;13(3):117-24 [2] [3] J. M. Wood, H. Decker et. al, Senile hair graying: H2O2‐mediated oxidative stress affects human hair color by blunting methionine sulfoxide repair, (July 2009), FASEB Journal. 23 (7): 2065–75.




